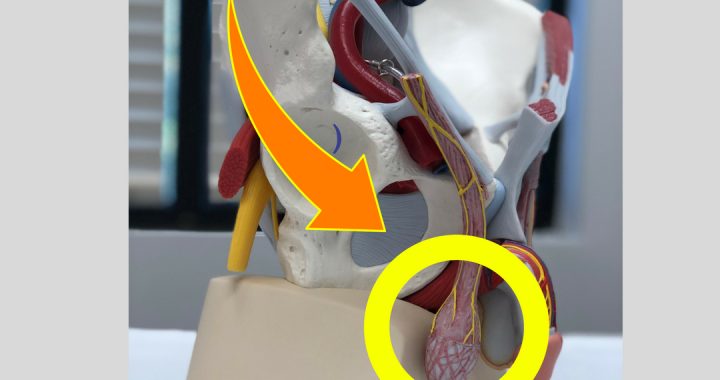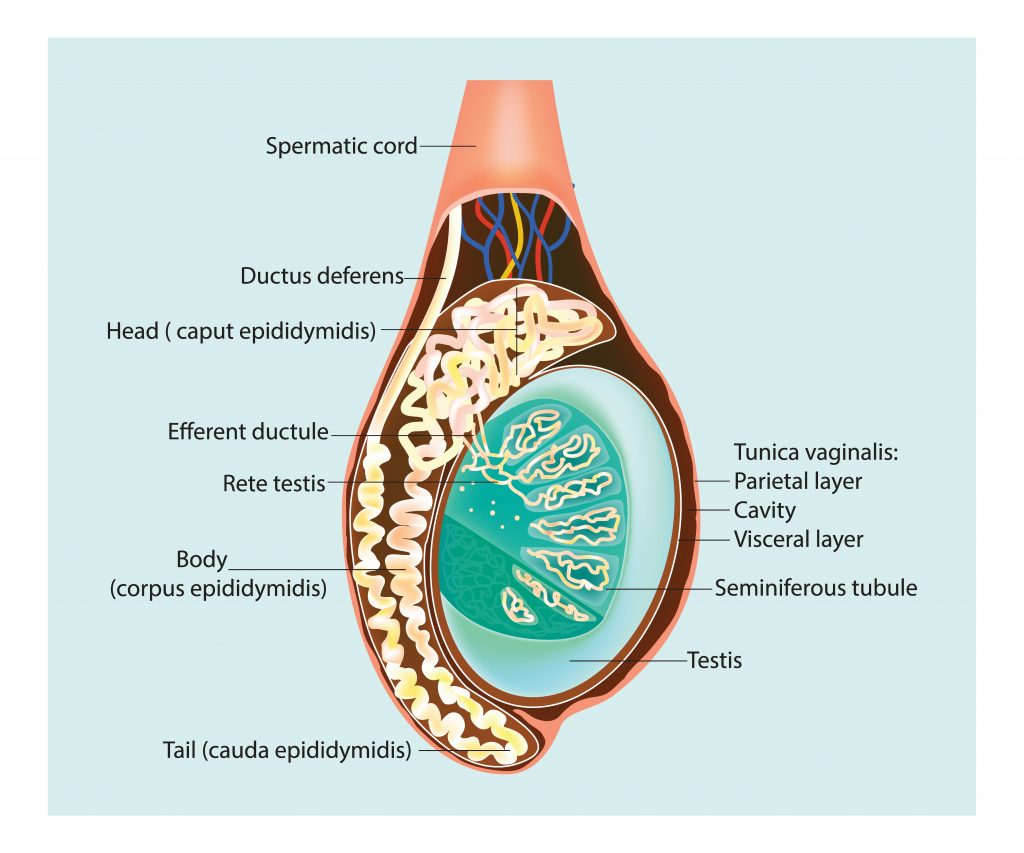
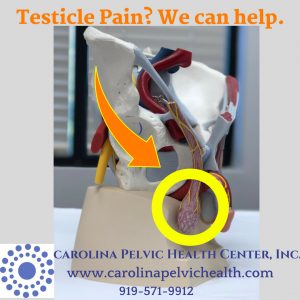
Many of our patients report pain in one or both testicles, the scrotum and perineum as their primary symptom or part of their pain. Intensity may vary from annoying and uncomfortable to constant and/ or severe pain that limits work, social and sexual activity.
Chronic testicular pain (CTP) affects at least 100,000 men/ year (1), and while most testicular pain has a clear cause, as many as 18-25% of men with CTP lack a clear diagnosis or treatment options for managing their symptoms (2). Often, men with CTP have sought help and relief without success, and sometimes after courses of antibiotics or medical/ surgical procedures (including testicle removal) without improvement in symptoms.
Sound familiar? If so, read on and learn more about how physical therapy might be able to help you learn more about your symptoms and get you some relief.
First things first: If you have acute testicle pain and haven’t seen your physician, start there. There’s lots of high end real estate in and around the scrotum and testicles. While pelvic PTs are highly skilled to screen and refer for non-musculoskeletal causes of all sorts of pain, it’s important to see your doctor to rule out more pressing medical causes, like infection, torsion, or tumor. We know it sounds scary, but it really is important to investigate to make sure that you get the right type of treatment.
Been there, done that: If you’ve been to the doctor and have either had treatment that has not been helpful, or are still unsure what is causing your symptoms, fear not. There may be some other factors to consider regarding your pain that are treatable and can lead you to relief.
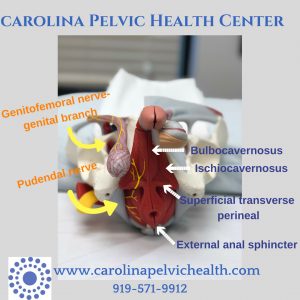 Mechanics & the musculoskeletal system: How you move, when you move, how much you move and what your dominant movement strategies are may all be factors in your symptoms. Your onset of pain may also be important. Did your pain start after doing a high intensity workout, groin strain or a new activity? It’s possible your muscle and/ or nerves may be involved and referring pain to the scrotum/ testicle region. A hernia may also be considered- these are easier to diagnose when a bulge is seen and/ or felt in the inguinal region; in some cases, you may have an occult or sports hernia, which may not have a bulge but can present with pain into the scrotum and testicles, pelvis and thigh.
Mechanics & the musculoskeletal system: How you move, when you move, how much you move and what your dominant movement strategies are may all be factors in your symptoms. Your onset of pain may also be important. Did your pain start after doing a high intensity workout, groin strain or a new activity? It’s possible your muscle and/ or nerves may be involved and referring pain to the scrotum/ testicle region. A hernia may also be considered- these are easier to diagnose when a bulge is seen and/ or felt in the inguinal region; in some cases, you may have an occult or sports hernia, which may not have a bulge but can present with pain into the scrotum and testicles, pelvis and thigh.
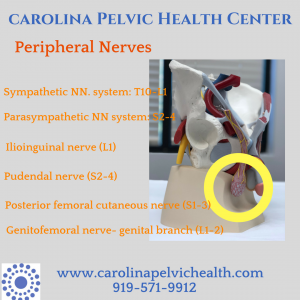 Central nervous system (CNS): Your brain and spinal cord are the masterminds of how we experience our environment. Hear a song on the radio that puts a smile on your face and brings you back in time to your glory days? Smell some homemade cooking that brings back memories of Grandma’s house? Think about sitting in your chair and your testicles start to ache? It sounds weird, but your brain and nervous system are tuned in to your environment so sharply that often we are unaware of those little connections that we associate throughout the day to sound, smells, sights and activities. When we have pain for longer than 3 months, our nervous system starts to adapt, becoming more protective of activities and sensations, resulting in a more sensitive response to what previously was a common and comfortable activity. If this continues to occur, pain may be increased and more often, and may occur with or without the mechanics we discussed above. ‘I don’t know what I did- it just started hurting’ or ‘I wish I knew what I did because today was a great day.’ The great news, is that we can treat the nervous system to address your symptoms! For this reason, treatment includes addressing both mechanics and the nervous system, via exercise, education, hands on treatment and modified or varied movement strategies when indicated.
Central nervous system (CNS): Your brain and spinal cord are the masterminds of how we experience our environment. Hear a song on the radio that puts a smile on your face and brings you back in time to your glory days? Smell some homemade cooking that brings back memories of Grandma’s house? Think about sitting in your chair and your testicles start to ache? It sounds weird, but your brain and nervous system are tuned in to your environment so sharply that often we are unaware of those little connections that we associate throughout the day to sound, smells, sights and activities. When we have pain for longer than 3 months, our nervous system starts to adapt, becoming more protective of activities and sensations, resulting in a more sensitive response to what previously was a common and comfortable activity. If this continues to occur, pain may be increased and more often, and may occur with or without the mechanics we discussed above. ‘I don’t know what I did- it just started hurting’ or ‘I wish I knew what I did because today was a great day.’ The great news, is that we can treat the nervous system to address your symptoms! For this reason, treatment includes addressing both mechanics and the nervous system, via exercise, education, hands on treatment and modified or varied movement strategies when indicated.
 If you are having pain in the scrotum or testicles and think PT may be right for you, call us at 919-571-9912 to schedule your first appointment! We also offer complimentary 15 minute phone consults to help you determine whether physical therapy can help.
If you are having pain in the scrotum or testicles and think PT may be right for you, call us at 919-571-9912 to schedule your first appointment! We also offer complimentary 15 minute phone consults to help you determine whether physical therapy can help.
References:
1.Calixte, N., Brahmbhatt, J. & Parekattil, S. Curr Urol Rep (2017) 18: 83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-017-0722-7
2.Am J Mens Health. 2013 Sep;7(5):402-13. doi: 10.1177/1557988313476732. Epub 2013 Feb (Chronic testicular pain in adult men: an integrative literature review).